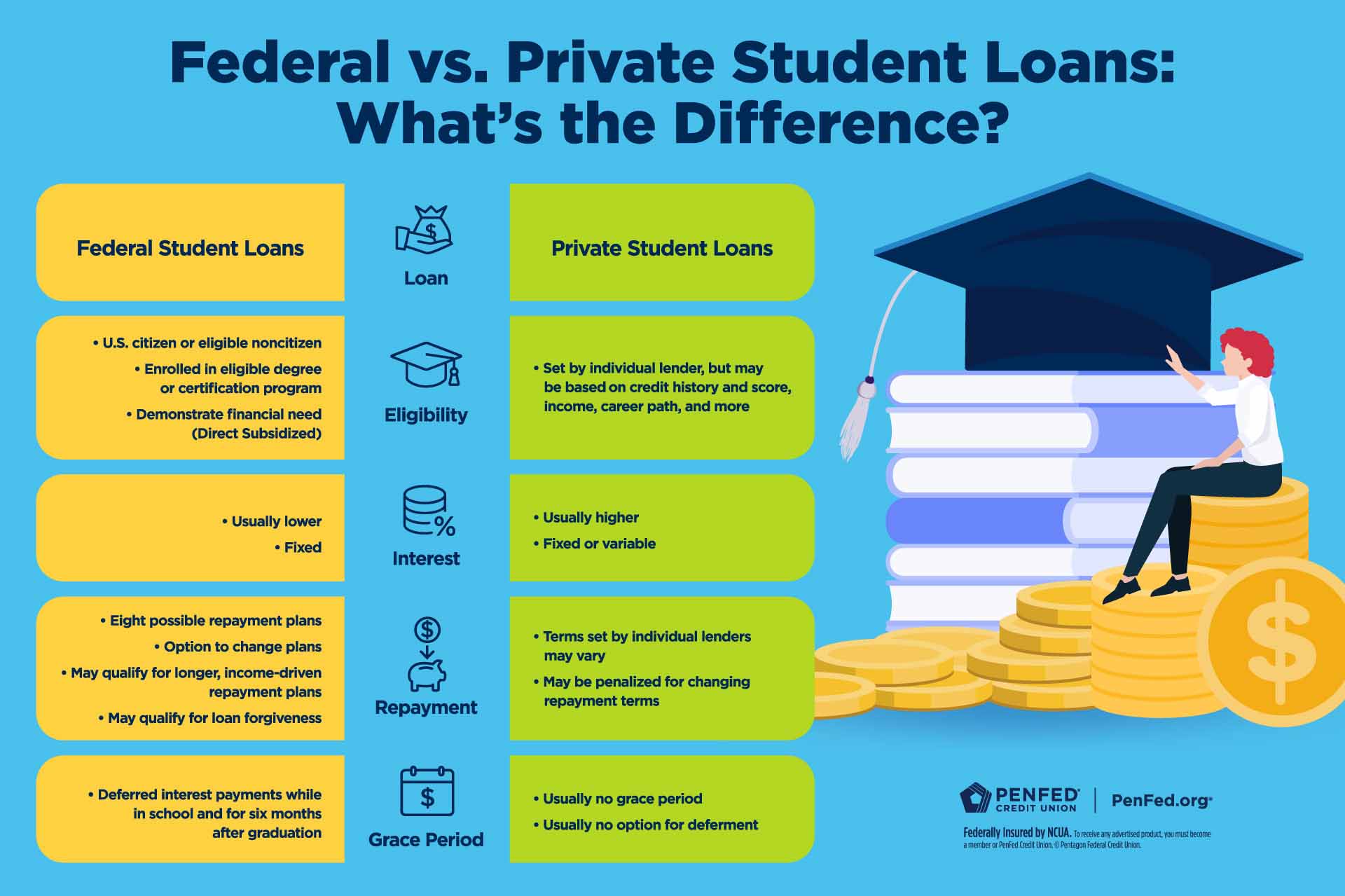
When it comes to financing your higher education, understanding the differences between private vs federal student loans is essential for making an informed decision. With tuition rates continuing to climb, students are often left wondering which loan option will offer the most benefits. While federal student loans are often the go-to choice, private student loans may sometimes be an alternative, depending on your financial situation and the loan terms you are looking for.
In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between private loans and federal loans, so you can determine which one is best suited to your educational financing needs.

Why Federal Loans Are Often the Better Choice
For most students, federal loans are the better option because they offer several advantages, including lower interest rates, more flexible repayment plans, and better borrower protections. Let’s explore these advantages in more detail.
Lower Interest Rates
One of the biggest advantages of federal loans is their lower interest rates. As of the 2024-2025 academic year, the interest rates for federal loans are as follows:
- Direct Subsidized Loans (undergraduate): 6.53%
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans (undergraduate): 6.53%
- PLUS Loans (graduate students and parents): 9.08%
In comparison, private loans tend to have higher interest rates that range from 4% to 18%, depending on the lender, your credit score, and other factors. While private loans may offer lower rates to students with excellent credit, these rates can vary and often come with the risk of increases in the future.

More Flexible Repayment Options
Another significant benefit of federal loans is the variety of repayment options they offer. Some of the most popular repayment options for federal loans include:
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: These plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income, making them ideal if your financial situation changes after you graduate.
- Graduated Repayment Plan: Payments start lower and gradually increase over time, which can be beneficial if you expect your income to grow.
- Extended Repayment Plan: This plan extends the repayment period, lowering monthly payments but potentially increasing the overall cost of the loan.
Private loans, on the other hand, tend to offer fewer flexible repayment options. Most private lenders require a fixed repayment schedule, which may not be adjustable based on your financial situation. If you encounter financial difficulty, you may have fewer options for relief.
No Credit Check Required
One of the biggest benefits of federal student loans is that most of them don’t require a credit check. This is a crucial factor, especially for students who have little to no credit history. Since federal loans are based on financial need rather than credit history, they are more accessible to a broader range of students.
In contrast, private loans require a credit check and are dependent on your credit score. If you have a low credit score or no credit history, it may be challenging to secure a private loan without a cosigner.
Loan Forgiveness Opportunities
One of the most significant advantages of federal loans is access to loan forgiveness programs. Federal loans are eligible for programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), which forgives your remaining loan balance after a set number of qualifying payments if you work in a public service job.
Unfortunately, private loans do not offer any forgiveness options. Regardless of your career or financial situation, you are required to repay the full amount borrowed.
Better Borrower Protections
Federal student loans offer more generous borrower protections compared to private loans. These protections include:
- Deferment and Forbearance: If you experience financial hardship, you may be able to temporarily pause payments without accruing additional fees or penalties.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: These allow for payments to be adjusted according to your income and family size, reducing the financial burden.
- Death and Disability Discharge: In the unfortunate event that a borrower passes away or becomes permanently disabled, federal student loans may be discharged, meaning the borrower or their family is no longer responsible for repayment.
These protections provide a safety net for borrowers who may encounter unexpected financial hardship.
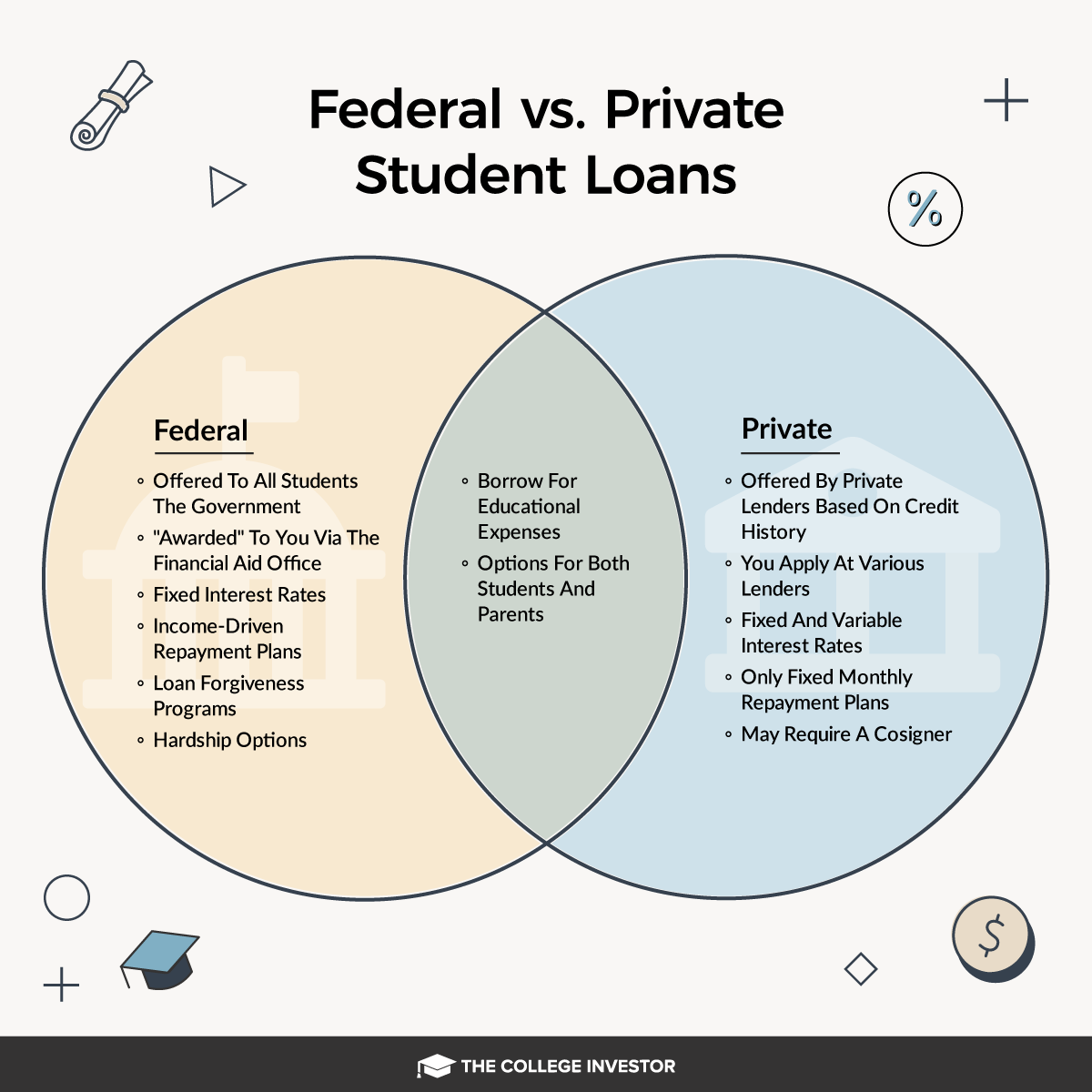
When Private Loans May Be Preferable
While federal loans offer a wide array of benefits, there are certain situations where private loans might be a better option. Here are a few circumstances where private loans may be preferable:
Higher Borrowing Limits
Private loans often allow you to borrow up to the total cost of attendance, which can be higher than the borrowing limits set by federal loans. Federal loans have annual limits based on your year in school, and they might not cover all the costs associated with attending an expensive school or pursuing specialized programs.
If you need to borrow more than the federal loan limits allow, private loans can help bridge the gap. However, be mindful of the higher interest rates and fewer protections that come with private loans.
Potentially Lower Rates for Excellent Credit
For students or parents with an excellent credit score, private loans may offer lower interest rates compared to federal loans. Private lenders often offer more competitive rates to those with high credit scores, which can lead to savings over the life of the loan.
However, keep in mind that private loans usually come with variable interest rates, meaning they could increase over time, adding uncertainty to the overall cost of your loan.
No Upfront Fees
Many private loans don’t charge origination fees, which can be an advantage over federal loans. For example, federal PLUS loans come with an origination fee that can range from 1.057% to 4.228% of the total loan amount, which adds to the cost of borrowing.
If you are looking to avoid these upfront fees, private loans might be a better option, but be sure to weigh this against the other costs and protections associated with private loans.
Conclusion
Choosing between private vs federal student loans depends on your specific financial needs and situation. For most students, federal loans offer lower interest rates, flexible repayment options, loan forgiveness programs, and strong borrower protections, making them the best option for financing your education. However, in certain cases—such as when you need to borrow more than federal limits or if you have an excellent credit score—private loans can serve as a valuable supplement.
It’s always recommended to exhaust federal loan options first, as they provide the most favorable terms and protections. If you need additional funding, consider private loans carefully, keeping in mind their higher interest rates and fewer borrower protections.
For more information on federal student loans, including how to apply, visit Federal Student Aid.